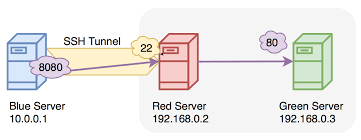
SSH tunneling, or SSH port forwarding, is a method of transporting arbitrary data over an encrypted SSH connection. SSH tunnels allow connections made to a local port (that is, to a port on your own desktop) to be forwarded to a remote machine via a secure channel.
To protect our network services, not all of them are reachable directly from outside the ENCS network. If you are offsite and need to access a resource that is protected in this way, you can use ssh to tunnel through an accessible resource to reach the protected resource. We generally recommend using the host “tunnel.encs.concordia.ca” for this purpose.
How to create an SSH Tunnel
Windows (PuTTy)
Install an SSH client such as PuTTy
In this example we will use PuTTy to create an SSH tunnel to the following remote hosts.
ssh tunnel.encs.concordia.ca -L 4040:remote_host1.encs.concordia.ca:5050
Where: 4040 is the local or Source port; remote_host1.encs.concordia.ca is the remote hostname; and 5050 is the remote port
- Launch PuTTy
- In the Category pane of the PuTTY Configuration window, expand Connection then expand SSH and select Tunnels.
- Under “Options controlling SSH port forwarding” enter the following:
- Source Port: 4040
- Destination: remote_host1.encs.concordia.ca:5050
- Source Port: 4040
- Click the Add button
- In the Category pane of the PuTTY Configuration window, click on Session
- Under “Basic options for your PuTTy session” enter:
- Hostname: tunnel.encs.concordia.ca
- Port: 22
- Saved Sessions: SSH Tunnel to remote_host1
- Click Save
- Click Open
- If you have not set up authorized_keys, then you will be prompted for your ENCS password in order to establish the tunnel.
- Do not close the PuTTy window
Repeat steps 3 and 4 to forward additional ports.